LeetCode题解(五) - N-Queens
题目难度:Hard
题目地址:No.51 N-Queens
题目描述:
The n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing n queens on an n×n chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
Given an integer n, return all distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle.
Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens' placement, where `Q` and `.` both indicate a queen and an empty space respectively.
Example:
Input: 4
Output: [
[".Q..", // Solution 1
"...Q",
"Q...",
"..Q."],
["..Q.", // Solution 2
"Q...",
"...Q",
".Q.."]
]
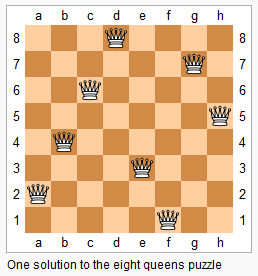
Explanation: There exist two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle as shown above.
本题为经典的N皇后问题,首先给定一个整数n,作为棋盘的维度n X n,根据西方象棋的规则,皇后可以攻击到其所在的某一行,某一列,以及左右对应的对角线。现在需要你根据输入,输出所有可行的,保证棋盘上n个皇后不会互相攻击的棋盘布局,以Q代表皇后,.代表空位。
题目思路:
-
N皇后问题是经典的搜索求解问题,最直观的写法,我们可以通过回溯迭代的方法,在每一步中根据规则限定矩阵逐渐生成可行解,在迭代终止时将可行解加入结果
vector中。此种方法也叫做在一定规则约束下的深度优先搜索算法,也可以称作为简单的启发式搜索算法。 -
但是实际上,此种方法需要考虑的位置组合情况较多,用于存储每一皇后位置的矩阵所需空间大。
dfs本身优化的关键就在于减少迭代函数的堆栈数,实际上可以通过初始位置的约束,来减少后续每一个皇后的位置的复杂组合,同时降低检测棋盘布局合理性的时间。 -
通过实验,初始状态下将每一个皇后初始放置于棋盘的对角线上,并且将记录皇后位置矩阵降低为1维,组合变换它们位置时只需交换两者数组值,同时检测对角线上的规则即可,很大程度上减少了操作时间数,以及存储空间大小。(Hint: 感谢LeetCode讨论区的神解答)
解法代码:
- 随机组合的约束DFS解法代码
class Solution { public: vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) { size = n; for(int i=0; i<n; i++){ vector<string> temp; vector<vector<bool>> enablePos; // Initialize the strings in each vector for(int j=0; j<n; j++){ string ttmp(n, '.'); vector<bool> bmp(n, true); temp.push_back(ttmp); enablePos.push_back(bmp); } // Recursive solving the possible positions generateSolution(temp, enablePos, 0, i); } return result; } void generateSolution(vector<string> temp, vector<vector<bool>> enablePos, int x, int y){ temp[x][y] = 'Q'; cout << "Yep" << x << y << endl; for(int i=0; i<size; i++){ enablePos[x][i] = false; // Disable the row enablePos[i][y] = false; // Disbale the column } // Left diagonal for(int i=y-1; i>=0&&x+y-i<size; i--) enablePos[x+y-i][i] = false; // Right diagonal for(int i=y+1; i<size&&x+i-y<size; i++) enablePos[x+i-y][i] = false; // Next step decision int target_row = x + 1; vector<int> enableIndex; if(target_row < size){ for(int i=0; i<size; i++){ if(enablePos[target_row][i] == true) enableIndex.push_back(i); } for(int i=0; i<enableIndex.size(); i++) generateSolution(temp, enablePos, target_row, enableIndex[i]); }else { result.push_back(temp); return; } } private: vector<vector<string>> result; int size; }; - 采用初始对角线布局,位置约束简化的DFS
class Solution { public: void dfs(vector<int>& board, int start, int n) { if (start == n) addToResult(board, n); for (int i = start; i < n; ++i) { swap(board[start], board[i]); if (checkValid(board, start, n)) dfs(board, start+1, n); swap(board[start], board[i]); } } // check the rows before the input row number for diagonal and anti-diagonal bool checkValid(vector<int>& board, int row, int n) { for (int i = -1; row+i>=0; --i) { if (board[row+i] == board[row]+i || board[row+i] == board[row]-i) return false; } return true; } void addToResult(vector<int>& board, int n) { vector<string> QD(n,string(n,'.')); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { QD[i][board[i]] = 'Q'; } res.push_back(move(QD)); } vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) { // sparse matrix: board[i] denotes the column number taken for the row vector<int> board; // initialize all queens on the diagonal (without sharing rows and columns) for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) board.push_back(i); dfs(board, 0, n); return res; } private: vector<vector<string>> res; };
运行结果:
-
随机组合的约束DFS解法代码
-
采用初始对角线布局,位置约束简化的DFS