Read source codes makes you better programming skills….
Go语言开发Web程序:UserCloud-Go 仓库地址
Golang net/http源码分析和功能介绍
一、net/http库实现http服务器的构建流程
一般来说,一个能够正常进行工作的http服务器需要实现以下的工作流程:
- 在当前主机上的某个端口开启监听程序(Socket),等待客户端的请求发起。
- 当客户端请求到来之时,接收该客户端的请求。
- 处理客户端请求,并返回相应的
Response报文。
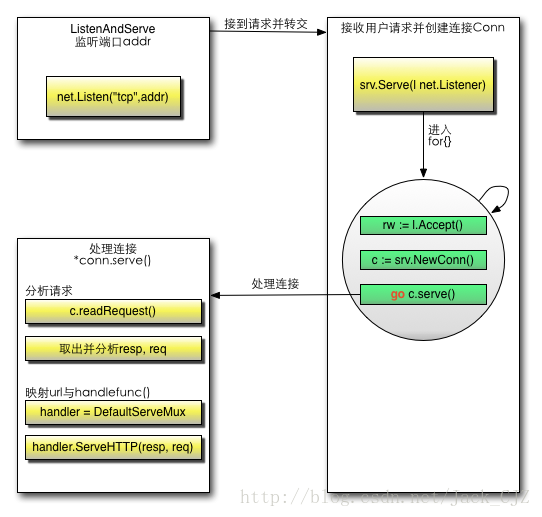
使用Go语言建立http服务器流程大致为:创建 ServerSocket,绑定并 listen,accept 连接,创建 go 线程服务一个连接。
监听主机上的某个端口,开启listen行为
// ListenAndServe listens on the TCP network address addr
// and then calls Serve with handler to handle requests
// on incoming connections.
// Accepted connections are configured to enable TCP keep-alives.
// Handler is typically nil, in which case the DefaultServeMux is used.
// ListenAndServe always returns a non-nil error.
func ListenAndServe(addr string, handler Handler) error {
server := &Server{Addr: addr, Handler: handler}
return server.ListenAndServe()
}
分析:该函数首先使用输入的端口号,以及处理函数Handler创建Server对象,然后调用Server对象的ListenAndServer方法,开启端口监听。
Server对象的ListenAndServer函数方法定义
// ListenAndServe listens on the TCP network address srv.Addr and then
// calls Serve to handle requests on incoming connections.
// Accepted connections are configured to enable TCP keep-alives.
// If srv.Addr is blank, ":http" is used.
// ListenAndServe always returns a non-nil error.
func (srv *Server) ListenAndServe() error {
addr := srv.Addr
if addr == "" {
addr = ":http"
}
ln, err := net.Listen("tcp", addr)
if err != nil {
return err
}
return srv.Serve(tcpKeepAliveListener{ln.(*net.TCPListener)})
}
分析:方法检测Server结构体内部的端口地址,若没有设置则赋值为http模式(即80端口监听模式)。紧接着调用net包内部的Listen(string, string)函数,调用TCP协议搭建底层服务,并且返回相应的Listener接口。最终根据该Listener接口ln,使用接口断言语法var.(type)转换为类型*net.TCPListener的结构体实例,通过该实例创建固定时间内保持TCP连接的tcpKeepAliveListener实例,调用Server结构体的Server函数监听客户端传来的数据。
补充:Listener接口定义
// A Listener is a generic network listener for stream-oriented protocols.
//
// Multiple goroutines may invoke methods on a Listener simultaneously.
type Listener interface {
// Accept waits for and returns the next connection to the listener.
Accept() (Conn, error)
// Close closes the listener.
// Any blocked Accept operations will be unblocked and return errors.
Close() error
// Addr returns the listener's network address.
Addr() Addr
}
分析:接口内部定义方法Accept(), Close(), Addr(),分别用于建立新连接并返回给Listener,关闭当前连接,以及返回接口当前所对应的网络地址。该接口定义了泛型的面向流传输协议的网络监听器,内部构建轻巧应用范围广。
接收Accept客户端请求
// Serve accepts incoming connections on the Listener l, creating a
// new service goroutine for each. The service goroutines read requests and
// then call srv.Handler to reply to them.
//
// For HTTP/2 support, srv.TLSConfig should be initialized to the
// provided listener's TLS Config before calling Serve. If
// srv.TLSConfig is non-nil and doesn't include the string "h2" in
// Config.NextProtos, HTTP/2 support is not enabled.
//
// Serve always returns a non-nil error. After Shutdown or Close, the
// returned error is ErrServerClosed.
func (srv *Server) Serve(l net.Listener) error {
defer l.Close()
if fn := testHookServerServe; fn != nil {
fn(srv, l)
}
var tempDelay time.Duration // how long to sleep on accept failure
if err := srv.setupHTTP2_Serve(); err != nil {
return err
}
srv.trackListener(l, true)
defer srv.trackListener(l, false)
baseCtx := context.Background() // base is always background, per Issue 16220
ctx := context.WithValue(baseCtx, ServerContextKey, srv)
for {
rw, e := l.Accept()
if e != nil {
select {
case <-srv.getDoneChan():
return ErrServerClosed
default:
}
if ne, ok := e.(net.Error); ok && ne.Temporary() {
if tempDelay == 0 {
tempDelay = 5 * time.Millisecond
} else {
tempDelay *= 2
}
if max := 1 * time.Second; tempDelay > max {
tempDelay = max
}
srv.logf("http: Accept error: %v; retrying in %v", e, tempDelay)
time.Sleep(tempDelay)
continue
}
return e
}
tempDelay = 0
c := srv.newConn(rw)
c.setState(c.rwc, StateNew) // before Serve can return
go c.serve(ctx)
}
}
分析:Server结构体方法Serve接收上文创建完成的,基于TCP协议的监听器接口net.Listener。本函数采取无限循环for{},在循环体内部不断接听客户端发来的请求,并且调用接口函数Accpet()接收请求,经由错误处理语句检测,检查无误之后,将请求信息rw赋值给当前Server结构体函数newConn(),创建新连接c,并且开启新线程goroutine,通过当前上下文信息,调用新连接的serve函数,执行处理客户端请求信息的功能。
补充:newConn()函数定义
// Create new connection from rwc.
func (srv *Server) newConn(rwc net.Conn) *conn {
c := &conn{
server: srv,
rwc: rwc,
}
if debugServerConnections {
c.rwc = newLoggingConn("server", c.rwc)
}
return c
}
分析:本函数创建与当前Server结构体内部连接内容相同的新连接,用于处理客户端请求。
创建go线程,运行新连接serve方法处理客户端请求,并返回响应报文
// Serve a new connection.
func (c *conn) serve(ctx context.Context) {
....
for {
w, err := c.readRequest(ctx)
if c.r.remain != c.server.initialReadLimitSize() {
// If we read any bytes off the wire, we're active.
c.setState(c.rwc, StateActive)
}
if err != nil {
const errorHeaders = "\r\nContent-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8\r\nConnection: close\r\n\r\n"
if err == errTooLarge {
// Their HTTP client may or may not be
// able to read this if we're
// responding to them and hanging up
// while they're still writing their
// request. Undefined behavior.
const publicErr = "431 Request Header Fields Too Large"
fmt.Fprintf(c.rwc, "HTTP/1.1 "+publicErr+errorHeaders+publicErr)
c.closeWriteAndWait()
return
}
if isCommonNetReadError(err) {
return // don't reply
}
publicErr := "400 Bad Request"
if v, ok := err.(badRequestError); ok {
publicErr = publicErr + ": " + string(v)
}
fmt.Fprintf(c.rwc, "HTTP/1.1 "+publicErr+errorHeaders+publicErr)
return
}
// Expect 100 Continue support
req := w.req
if req.expectsContinue() {
if req.ProtoAtLeast(1, 1) && req.ContentLength != 0 {
// Wrap the Body reader with one that replies on the connection
req.Body = &expectContinueReader{readCloser: req.Body, resp: w}
}
} else if req.Header.get("Expect") != "" {
w.sendExpectationFailed()
return
}
c.curReq.Store(w)
if requestBodyRemains(req.Body) {
registerOnHitEOF(req.Body, w.conn.r.startBackgroundRead)
} else {
w.conn.r.startBackgroundRead()
}
// HTTP cannot have multiple simultaneous active requests.[*]
// Until the server replies to this request, it can't read another,
// so we might as well run the handler in this goroutine.
// [*] Not strictly true: HTTP pipelining. We could let them all process
// in parallel even if their responses need to be serialized.
// But we're not going to implement HTTP pipelining because it
// was never deployed in the wild and the answer is HTTP/2.
serverHandler{c.server}.ServeHTTP(w, w.req)
w.cancelCtx()
if c.hijacked() {
return
}
w.finishRequest()
....
分析:上述代码篇幅较长,此处为了简化分析,只提取核心操作进行解读。
w, err := c.readRequest(ctx),基于当前上下文对象,取出连接实例中相应的请求信息w。serverHandler{c.server}.ServeHTTP(w, w.req),通过传入当前连接的server成员,创建serverHandler结构体,同时调用其ServerHTTP()方法,首先对客户端URL进行解析跳转到不同的处理函数,再对前面解析的请求信息进行处理。w.finishRequest()完成处理请求过程,返回相应的Response报文。
二、 细节阅读 – net/http库ServeMux解读
基于HTTP请求的路由管理器ServeMux,匹配不同请求的不同URL,进行不同Handler映射
type ServeMux struct {
mu sync.RWMutex
m map[string]muxEntry
es []muxEntry // slice of entries sorted from longest to shortest.
hosts bool // whether any patterns contain hostnames
}
// Definition of muxEntry
type muxEntry struct {
h Handler
pattern string
}
分析:首先ServerMux内部含有用于同步操作的RW锁成员mu,其次成员m为map(string -> muxEntry),使一个用于记录请求path与相应的Handler对应关系的map对象。此处还有es成员,是一个muxEntry切片,此处注释提醒我们改切片通过pattern匹配路径长度进行最长到最短的排序,排序的目的是为了在进行路由URL匹配时能够匹配到最接近的Handler(精确匹配到符合条件路由)。最后一个成员说明匹配路径是否包含hostname。
通过ServeMux实例进行路径匹配函数调用,接收相关路径,返回对应的处理函数
// Find a handler on a handler map given a path string.
// Most-specific (longest) pattern wins.
func (mux *ServeMux) match(path string) (h Handler, pattern string) {
// Check for exact match first.
v, ok := mux.m[path]
if ok {
return v.h, v.pattern
}
// Check for longest valid match. mux.es contains all patterns
// that end in / sorted from longest to shortest.
for _, e := range mux.es {
if strings.HasPrefix(path, e.pattern) {
return e.h, e.pattern
}
}
return nil, ""
}
分析:此处首先利用map成员进行初次匹配,输入路径字符串马上搜索到对应的muxEntry对象并返回其内容。其次,若出现错误,那么进行二次匹配,遍历当前所有muxEntry切片,对元素进行前缀匹配strings.HasPrefix(path, e.pattern),返回相应结果。